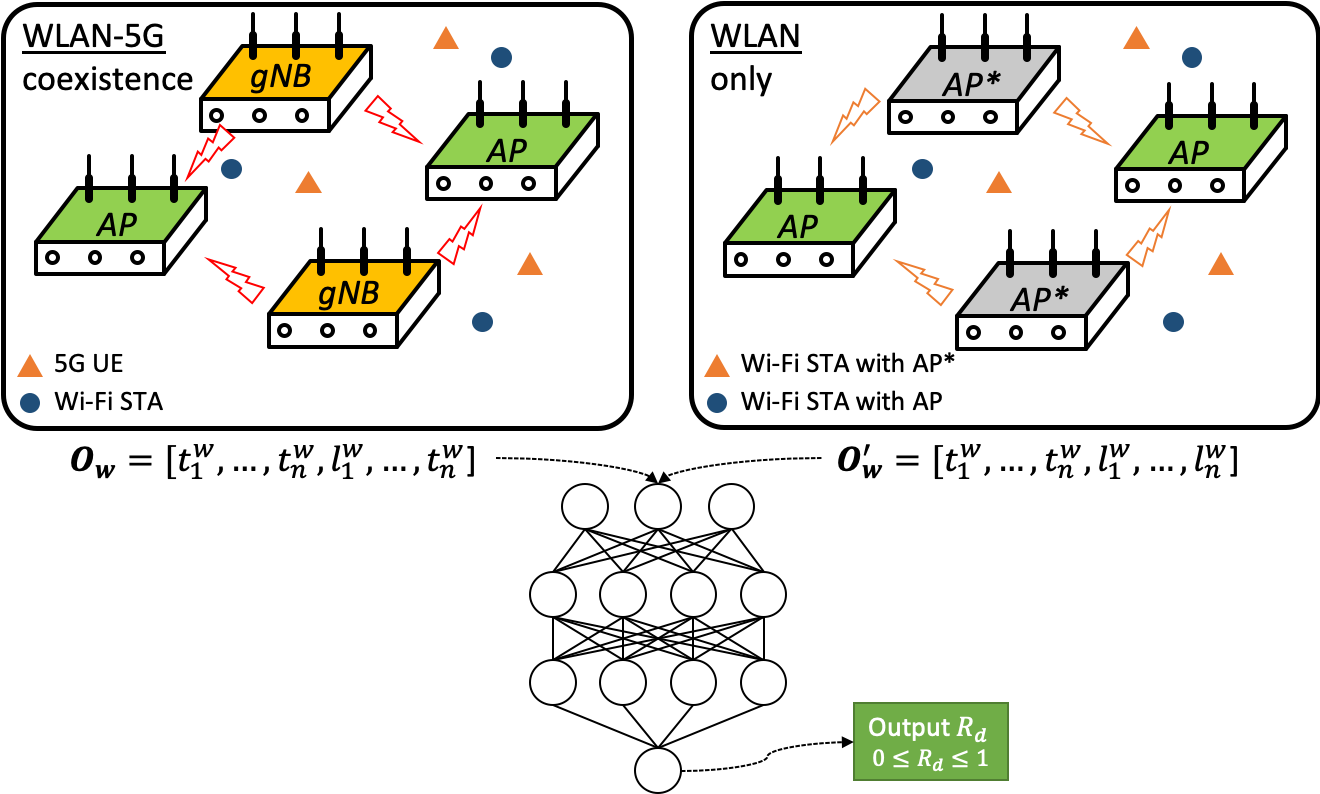
The WMNL is investigating AI/ML-empowered approaches to various networking problems. For example, we re-visited the WLAN-5G coexistence scenario to adopt AI techniques for autonomous network reconfiguration. In the WLAN-5G heterogeneous network (HetNet), an asymmetry can arise such that Wi-Fi is exposed to 5G NR-U, but NR-U is hidden from Wi-Fi, since Wi-Fi’s CCA threshold is -62 dBm whereas NR-U’s is -72 dBm, as directed by 3GPP. Although we have already proposed a series of analytical frameworks to model such asymmetry (in our TMC’18 and Access’19 papers), we also consider to utilize AI techniques likes Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) and Generative adversarial network (GAN) to achieve a more generic and versatile coexistence mechanism, as illustrated below.
We are also looking at various technology-enablers of 6G, including RAN-agnostic communications, semantic communications, geographical federated learning (FL), etc. In particular, RAN-agnostic communications can unleash a completely new set of ways to utilize unlicensed bands for 6G, by enabling RAN-agnostic devices to identify the intrinsic features (e.g., modulation) of an incompatible signal by the help of state-of-the-art AI techniques. In this way, various incompatible standards (e.g., 6G, WLAN, 5G NR-U, BLE, MulteFire, etc.) in the unlicensed bands can achieve near-optimal coexistence even without exchanging any information among them.
Since 6G is expected to be much spectrum-craving more than ever,RAN-agnostic communications will play a crucial role in realizing 6G’s efficient utilization of unlicensed bands with peaceful coexistence with other incumbent standards. To fulfill such a goal, WMNL has developed RiSi, a novel neural network model for RAN-agnostic identification of incompatible OFDMA signals as shown below. More details can be found from our arXiv paper (arXiv:2211.12287), available at https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.12287.pdf.